In the past few years, 3D printing has evolved the manufacturing sector, making it possible to make difficult objects with convenience. Central to this technology are the constituents called 3D printing filaments. Such filaments come in an extensive range of kinds and properties, each suitable for diverse applications.
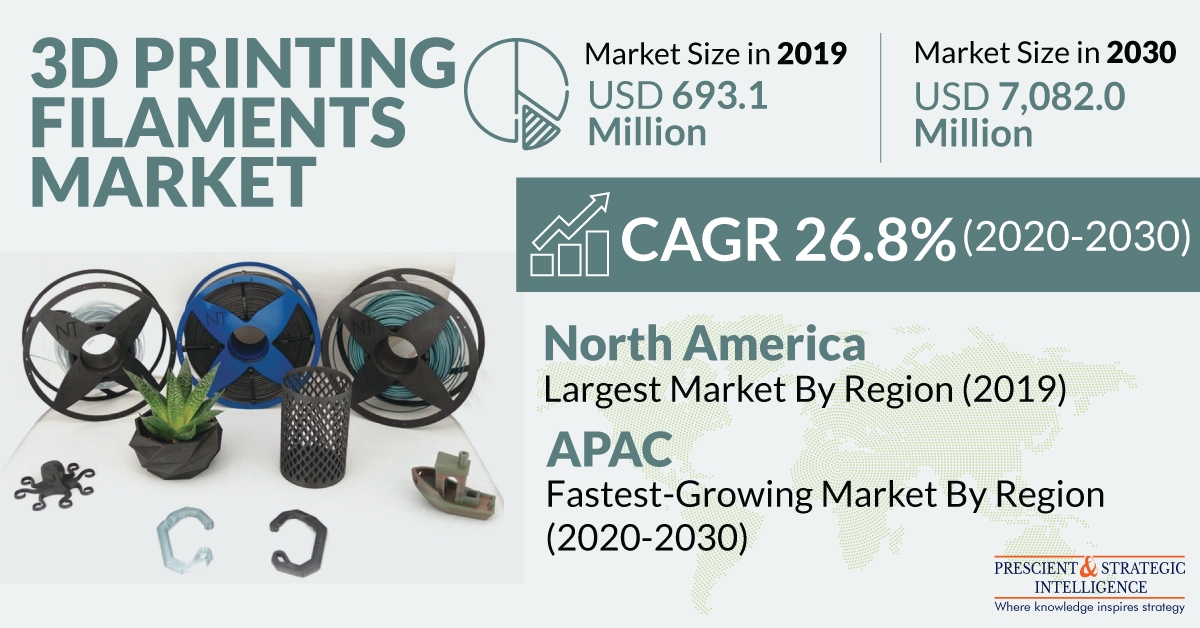
The 3D printing filaments market is experiencing growth and is projected to reach USD 7,082.0 million by 2030.
Polylactic Acid (PLA)
One of the most common options among 3D printing users is PLA filament. Resulting from renewable resources such as sugarcane and cornstarch, PLA is decomposable and ecologically friendly. It is simple to print with, needing low printing temperatures and negligible warping. PLA is often utilized for decorative objects, prototyping, and low-stress applications.
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene Filament
ABS (acrylonitrile butadiene styrene) is probably the most common filament used in 3D printing. It is especially valuable in strong plastic parts that must remain resilient in the face of temperature swings. It is mainly used in FDM (fused deposition modeling) 3D printers. ABS is a thermoplastic polymer composed of three monomers: acrylonitrile, butadiene, and styrene. The material was first patented in the 1940s and very quickly gained popularity.
ABS is used in many industries today because of its flexibility, moldability, and strength.
Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol Filament
PETG filament provides stability between the convenience of printing and material properties. It is popular for its flexibility, toughness, and resistance to moisture. Not like ABS and PLA, PETG is translucent and provides outstanding layer adhesion, making it appropriate for working with containers, mechanical parts, and medical devices.
Nylon 3D printing filament also has some negative properties. It is prone to warping – a result of the material crystallizing
Specialty Filaments
Furthermore, to the above-stated filaments, the world of 3D printing provides a variety of specialty filaments. Such comprises glow-in-the-dark filaments, wood-infused filaments and metal-filled filaments, and more.
These unique filaments permit the making of objects with characteristic finishes, textures, and properties, increasing the potential of 3D printing.
The varied variety of 3D printing filaments obtainable presently has opened up new gates for innovation and creativity. Every filament kind provides unique characteristics that cater to different applications and user needs.