Continuous Delivery: Security Considerations
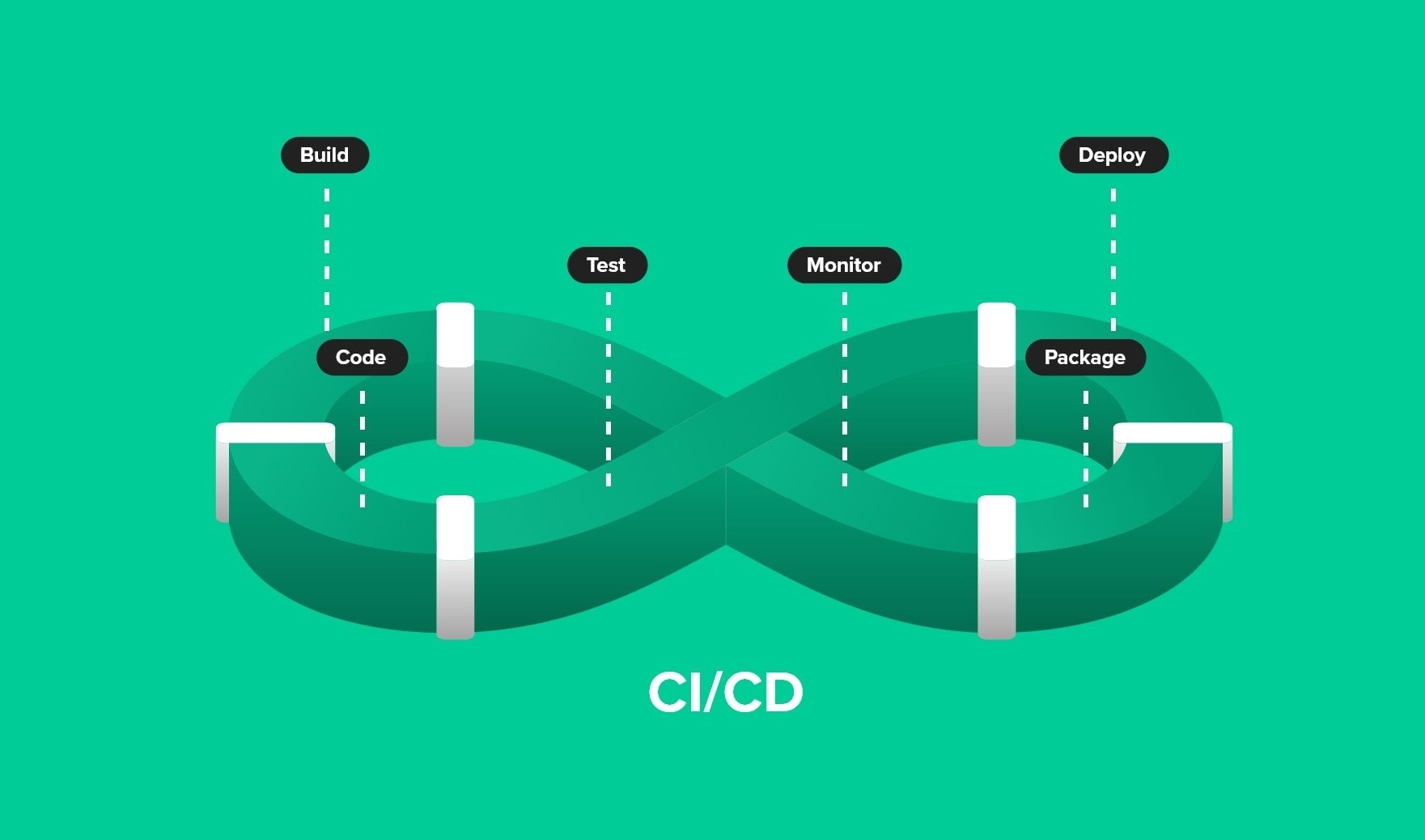
Continuous Delivery (CD) is a software development practice where code changes are automatically prepared for a release to production. It extends Continuous Integration (CI) by ensuring that the software can be reliably released at any time. This practice aims to make deployments predictable and routine, so that new features, configurations, and bug fixes can be delivered to users quickly and sustainably.
The Continuous Delivery market is experiencing significant growth, driven by the increasing adoption of cloud-based solutions and the need for faster, more reliable software deployment processes. As of 2022, the market was valued at approximately $3.12 billion and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 17.81%, reaching nearly $9.83 billion by 2029. This growth is fueled by the benefits of Continuous Delivery, such as improved product quality, reduced time to market, and enhanced operational efficiency. Organizations across various sectors, including IT, healthcare, and finance, are investing in Continuous Delivery tools and services to streamline their development pipelines and stay competitive in a rapidly evolving digital landscape.
Key Principles of Continuous Delivery
Automated Testing: One of the core principles of Continuous Delivery is the use of automated tests to ensure that code changes do not break the existing functionality. This includes unit tests, integration tests, and end-to-end tests. Automated testing helps in identifying issues early in the development cycle, reducing the risk of defects in production.
Continuous Integration: CI is a practice where developers frequently integrate their code changes into a shared repository. Each integration is verified by an automated build and tests, allowing teams to detect problems early. CI is a prerequisite for CD, as it ensures that the codebase is always in a deployable state.
Automated Deployment: CD involves automating the deployment process to ensure that software can be released to production at any time. This includes automating the steps required to deploy the application, such as provisioning infrastructure, configuring environments, and deploying code.
Version Control: All code changes, configurations, and scripts are stored in a version control system. This ensures that there is a single source of truth for the entire codebase, making it easier to track changes, collaborate with team members, and roll back to previous versions if necessary.
Monitoring and Feedback: Continuous monitoring of the application in production is essential to detect issues and gather feedback. This includes monitoring performance, error rates, and user behaviour. Feedback from monitoring helps in making informed decisions about future releases and improvements.
Continuous Delivery is a powerful practice that can transform the way software is developed and delivered. By automating the testing, integration, and deployment processes, CD enables teams to deliver high-quality software quickly and reliably. This not only improves the efficiency and effectiveness of the development process but also provides significant business benefits, such as faster time to market, improved quality.
Continuous Delivery (CD) is a software development practice where code changes are automatically prepared for a release to production. It extends Continuous Integration (CI) by ensuring that the software can be reliably released at any time. This practice aims to make deployments predictable and routine, so that new features, configurations, and bug fixes can be delivered to users quickly and sustainably.
The Continuous Delivery market is experiencing significant growth, driven by the increasing adoption of cloud-based solutions and the need for faster, more reliable software deployment processes. As of 2022, the market was valued at approximately $3.12 billion and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 17.81%, reaching nearly $9.83 billion by 2029. This growth is fueled by the benefits of Continuous Delivery, such as improved product quality, reduced time to market, and enhanced operational efficiency. Organizations across various sectors, including IT, healthcare, and finance, are investing in Continuous Delivery tools and services to streamline their development pipelines and stay competitive in a rapidly evolving digital landscape.
Key Principles of Continuous Delivery
Automated Testing: One of the core principles of Continuous Delivery is the use of automated tests to ensure that code changes do not break the existing functionality. This includes unit tests, integration tests, and end-to-end tests. Automated testing helps in identifying issues early in the development cycle, reducing the risk of defects in production.
Continuous Integration: CI is a practice where developers frequently integrate their code changes into a shared repository. Each integration is verified by an automated build and tests, allowing teams to detect problems early. CI is a prerequisite for CD, as it ensures that the codebase is always in a deployable state.
Automated Deployment: CD involves automating the deployment process to ensure that software can be released to production at any time. This includes automating the steps required to deploy the application, such as provisioning infrastructure, configuring environments, and deploying code.
Version Control: All code changes, configurations, and scripts are stored in a version control system. This ensures that there is a single source of truth for the entire codebase, making it easier to track changes, collaborate with team members, and roll back to previous versions if necessary.
Monitoring and Feedback: Continuous monitoring of the application in production is essential to detect issues and gather feedback. This includes monitoring performance, error rates, and user behaviour. Feedback from monitoring helps in making informed decisions about future releases and improvements.
Continuous Delivery is a powerful practice that can transform the way software is developed and delivered. By automating the testing, integration, and deployment processes, CD enables teams to deliver high-quality software quickly and reliably. This not only improves the efficiency and effectiveness of the development process but also provides significant business benefits, such as faster time to market, improved quality.
Continuous Delivery: Security Considerations
Continuous Delivery (CD) is a software development practice where code changes are automatically prepared for a release to production. It extends Continuous Integration (CI) by ensuring that the software can be reliably released at any time. This practice aims to make deployments predictable and routine, so that new features, configurations, and bug fixes can be delivered to users quickly and sustainably.
The Continuous Delivery market is experiencing significant growth, driven by the increasing adoption of cloud-based solutions and the need for faster, more reliable software deployment processes. As of 2022, the market was valued at approximately $3.12 billion and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 17.81%, reaching nearly $9.83 billion by 2029. This growth is fueled by the benefits of Continuous Delivery, such as improved product quality, reduced time to market, and enhanced operational efficiency. Organizations across various sectors, including IT, healthcare, and finance, are investing in Continuous Delivery tools and services to streamline their development pipelines and stay competitive in a rapidly evolving digital landscape.
Key Principles of Continuous Delivery
Automated Testing: One of the core principles of Continuous Delivery is the use of automated tests to ensure that code changes do not break the existing functionality. This includes unit tests, integration tests, and end-to-end tests. Automated testing helps in identifying issues early in the development cycle, reducing the risk of defects in production.
Continuous Integration: CI is a practice where developers frequently integrate their code changes into a shared repository. Each integration is verified by an automated build and tests, allowing teams to detect problems early. CI is a prerequisite for CD, as it ensures that the codebase is always in a deployable state.
Automated Deployment: CD involves automating the deployment process to ensure that software can be released to production at any time. This includes automating the steps required to deploy the application, such as provisioning infrastructure, configuring environments, and deploying code.
Version Control: All code changes, configurations, and scripts are stored in a version control system. This ensures that there is a single source of truth for the entire codebase, making it easier to track changes, collaborate with team members, and roll back to previous versions if necessary.
Monitoring and Feedback: Continuous monitoring of the application in production is essential to detect issues and gather feedback. This includes monitoring performance, error rates, and user behaviour. Feedback from monitoring helps in making informed decisions about future releases and improvements.
Continuous Delivery is a powerful practice that can transform the way software is developed and delivered. By automating the testing, integration, and deployment processes, CD enables teams to deliver high-quality software quickly and reliably. This not only improves the efficiency and effectiveness of the development process but also provides significant business benefits, such as faster time to market, improved quality.
0 Kommentare
0 Anteile