Vertical Cavity Surface Emitting Laser: Role in Scientific Research
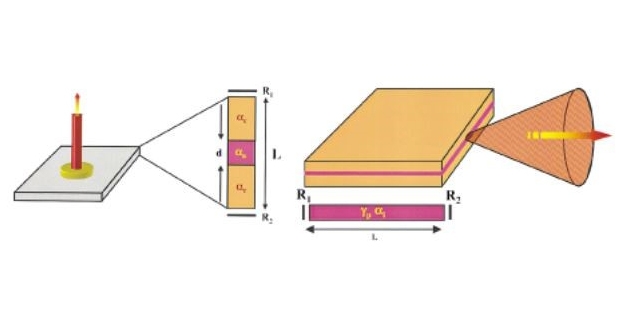
Vertical Cavity Surface Emitting Lasers (VCSELs) are a class of semiconductor lasers that emit light perpendicular to the surface of the wafer, unlike traditional edge-emitting lasers that emit light along the plane of the wafer. This unique characteristic allows for several advantages, including easier manufacturing, testing, and integration into various optical systems. VCSELs have become increasingly important in a wide range of applications, from data communication and sensing to industrial and medical uses.
One of the primary advantages of Vertical Cavity Surface Emitting Lasers is their ability to be manufactured in large arrays on a single wafer, significantly reducing production costs and enhancing scalability. This manufacturing process also allows for on-wafer testing, where each VCSEL can be individually tested before being cut from the wafer, ensuring high-quality output and reducing waste. Additionally, VCSELs can be easily integrated with other optical components, making them ideal for compact and efficient optical systems.
VCSELs are particularly well-suited for data communication applications, where they are used in fiber optic networks to transmit data at high speeds. Their ability to operate at wavelengths compatible with standard optical fibers, combined with their high modulation speeds, makes VCSELs an excellent choice for high-speed data transmission. This capability is crucial for meeting the ever-increasing demand for bandwidth in data centers, telecommunication networks, and the internet.
Beyond data communication, Vertical Cavity Surface Emitting Lasers are also used in a variety of sensing applications. In consumer electronics, VCSELs are commonly found in devices like smartphones for facial recognition and proximity sensing. Their compact size, low power consumption, and ability to generate precise and consistent light beams make them ideal for these applications. In the automotive industry, VCSELs are used in advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) and LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) systems for autonomous vehicles, providing accurate distance measurements and enhancing vehicle safety.
As technology continues to advance, the future of VCSELs looks promising, with ongoing research focused on improving their performance and expanding their applications. Innovations in materials and fabrication techniques are expected to enhance the efficiency and output power of VCSELs, making them even more versatile and capable. Moreover, the integration of VCSELs with emerging technologies like 5G, Internet of Things (IoT), and augmented reality (AR) will further drive their adoption and impact across various industries.
In conclusion, Vertical Cavity Surface Emitting Lasers (VCSELs) are a versatile and efficient class of semiconductor lasers with a wide range of applications. Their unique manufacturing process, high-speed data transmission capabilities, and suitability for sensing applications make them an essential component in modern optical systems. With continued advancements in technology, VCSELs are poised to play an even more significant role in shaping the future of communication, sensing, and beyond.
https://www.marketdigits.com/vertical-cavity-surface-emitting-laser-vcsel-market
Vertical Cavity Surface Emitting Lasers (VCSELs) are a class of semiconductor lasers that emit light perpendicular to the surface of the wafer, unlike traditional edge-emitting lasers that emit light along the plane of the wafer. This unique characteristic allows for several advantages, including easier manufacturing, testing, and integration into various optical systems. VCSELs have become increasingly important in a wide range of applications, from data communication and sensing to industrial and medical uses.
One of the primary advantages of Vertical Cavity Surface Emitting Lasers is their ability to be manufactured in large arrays on a single wafer, significantly reducing production costs and enhancing scalability. This manufacturing process also allows for on-wafer testing, where each VCSEL can be individually tested before being cut from the wafer, ensuring high-quality output and reducing waste. Additionally, VCSELs can be easily integrated with other optical components, making them ideal for compact and efficient optical systems.
VCSELs are particularly well-suited for data communication applications, where they are used in fiber optic networks to transmit data at high speeds. Their ability to operate at wavelengths compatible with standard optical fibers, combined with their high modulation speeds, makes VCSELs an excellent choice for high-speed data transmission. This capability is crucial for meeting the ever-increasing demand for bandwidth in data centers, telecommunication networks, and the internet.
Beyond data communication, Vertical Cavity Surface Emitting Lasers are also used in a variety of sensing applications. In consumer electronics, VCSELs are commonly found in devices like smartphones for facial recognition and proximity sensing. Their compact size, low power consumption, and ability to generate precise and consistent light beams make them ideal for these applications. In the automotive industry, VCSELs are used in advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) and LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) systems for autonomous vehicles, providing accurate distance measurements and enhancing vehicle safety.
As technology continues to advance, the future of VCSELs looks promising, with ongoing research focused on improving their performance and expanding their applications. Innovations in materials and fabrication techniques are expected to enhance the efficiency and output power of VCSELs, making them even more versatile and capable. Moreover, the integration of VCSELs with emerging technologies like 5G, Internet of Things (IoT), and augmented reality (AR) will further drive their adoption and impact across various industries.
In conclusion, Vertical Cavity Surface Emitting Lasers (VCSELs) are a versatile and efficient class of semiconductor lasers with a wide range of applications. Their unique manufacturing process, high-speed data transmission capabilities, and suitability for sensing applications make them an essential component in modern optical systems. With continued advancements in technology, VCSELs are poised to play an even more significant role in shaping the future of communication, sensing, and beyond.
https://www.marketdigits.com/vertical-cavity-surface-emitting-laser-vcsel-market
Vertical Cavity Surface Emitting Laser: Role in Scientific Research
Vertical Cavity Surface Emitting Lasers (VCSELs) are a class of semiconductor lasers that emit light perpendicular to the surface of the wafer, unlike traditional edge-emitting lasers that emit light along the plane of the wafer. This unique characteristic allows for several advantages, including easier manufacturing, testing, and integration into various optical systems. VCSELs have become increasingly important in a wide range of applications, from data communication and sensing to industrial and medical uses.
One of the primary advantages of Vertical Cavity Surface Emitting Lasers is their ability to be manufactured in large arrays on a single wafer, significantly reducing production costs and enhancing scalability. This manufacturing process also allows for on-wafer testing, where each VCSEL can be individually tested before being cut from the wafer, ensuring high-quality output and reducing waste. Additionally, VCSELs can be easily integrated with other optical components, making them ideal for compact and efficient optical systems.
VCSELs are particularly well-suited for data communication applications, where they are used in fiber optic networks to transmit data at high speeds. Their ability to operate at wavelengths compatible with standard optical fibers, combined with their high modulation speeds, makes VCSELs an excellent choice for high-speed data transmission. This capability is crucial for meeting the ever-increasing demand for bandwidth in data centers, telecommunication networks, and the internet.
Beyond data communication, Vertical Cavity Surface Emitting Lasers are also used in a variety of sensing applications. In consumer electronics, VCSELs are commonly found in devices like smartphones for facial recognition and proximity sensing. Their compact size, low power consumption, and ability to generate precise and consistent light beams make them ideal for these applications. In the automotive industry, VCSELs are used in advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) and LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) systems for autonomous vehicles, providing accurate distance measurements and enhancing vehicle safety.
As technology continues to advance, the future of VCSELs looks promising, with ongoing research focused on improving their performance and expanding their applications. Innovations in materials and fabrication techniques are expected to enhance the efficiency and output power of VCSELs, making them even more versatile and capable. Moreover, the integration of VCSELs with emerging technologies like 5G, Internet of Things (IoT), and augmented reality (AR) will further drive their adoption and impact across various industries.
In conclusion, Vertical Cavity Surface Emitting Lasers (VCSELs) are a versatile and efficient class of semiconductor lasers with a wide range of applications. Their unique manufacturing process, high-speed data transmission capabilities, and suitability for sensing applications make them an essential component in modern optical systems. With continued advancements in technology, VCSELs are poised to play an even more significant role in shaping the future of communication, sensing, and beyond.
https://www.marketdigits.com/vertical-cavity-surface-emitting-laser-vcsel-market
0 Comments
0 Shares