Optical Transceiver Trends in Cloud Computing
Optical transceivers are pivotal components in modern communication networks, facilitating the seamless transmission and reception of data over optical fibre. These devices convert electrical signals into optical signals for transmission and then back into electrical signals for reception, enabling high-speed data transfer over long distances with minimal signal loss. The versatility and efficiency of optical transceivers make them indispensable in various applications, including data centers, telecommunications, and enterprise networks.
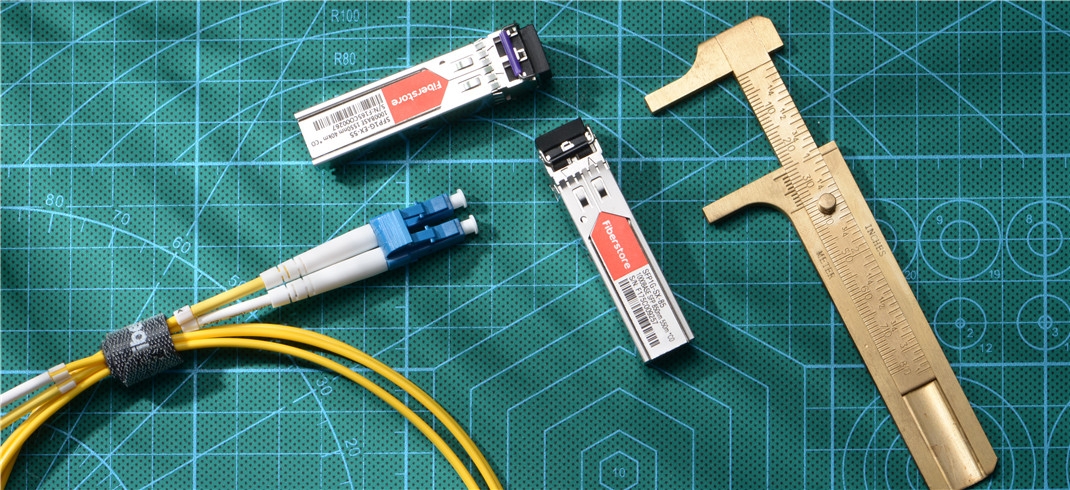
There are several types of optical transceivers, each tailored for specific performance requirements. The Small Form-factor Pluggable (SFP) transceivers are compact and hot-swappable, supporting speeds up to 4.25 Gbps, while the enhanced SFP+ version supports higher data rates up to 10 Gbps, commonly used in 10 Gigabit Ethernet applications. The Quad Small Form-factor Pluggable (QSFP) transceivers support four channels of data in one module, making them suitable for high-density applications, with QSFP+ and QSFP28 supporting 40 Gbps and 100 Gbps, respectively. The C Form-factor Pluggable (CFP) transceivers are designed for high-speed digital signal transmission, supporting data rates up to 100 Gbps.
Optical transceivers offer several key benefits, including high data rates, long-distance transmission, scalability, and low latency. They support data rates ranging from 1 Gbps to 400 Gbps, enabling fast and efficient data transfer. Their ability to transmit data over long distances, up to several kilometres, without significant signal degradation, makes them ideal for wide-area networks (WANs). The modular and hot-swappable nature of optical transceivers allows for easy upgrades and scalability in network infrastructure, while the low latency of optical fibre communication is critical for applications requiring real-time data transmission, such as financial trading and video conferencing. Optical transceivers are used in a variety of applications, including data centers, telecommunications, and enterprise networks.
In data centers, they are essential for connecting servers, storage systems, and networking equipment, ensuring high-speed data transfer and efficient network performance. In telecommunications, optical transceivers are used in backbone networks to transmit data over long distances, supporting high-speed internet and communication services. Businesses use optical transceivers in enterprise networks to connect different parts of their network infrastructure, ensuring reliable and fast communication between departments and locations. The demand for optical transceivers is expected to grow, driven by the increasing need for high-speed data transmission and the expansion of 5G networks. Innovations in optical transceiver technology, such as the development of 800 Gbps transceivers, will further enhance network performance and support the growing data demands of modern applications.
In conclusion, optical transceivers are vital components in today’s communication networks, offering high-speed data transfer, long-distance transmission, and scalability. As technology advances, these devices will continue to play a crucial role in enabling efficient and reliable communication across various industries.
Optical Transceiver Trends in Cloud Computing
Optical transceivers are pivotal components in modern communication networks, facilitating the seamless transmission and reception of data over optical fibre. These devices convert electrical signals into optical signals for transmission and then back into electrical signals for reception, enabling high-speed data transfer over long distances with minimal signal loss. The versatility and efficiency of optical transceivers make them indispensable in various applications, including data centers, telecommunications, and enterprise networks.
There are several types of optical transceivers, each tailored for specific performance requirements. The Small Form-factor Pluggable (SFP) transceivers are compact and hot-swappable, supporting speeds up to 4.25 Gbps, while the enhanced SFP+ version supports higher data rates up to 10 Gbps, commonly used in 10 Gigabit Ethernet applications. The Quad Small Form-factor Pluggable (QSFP) transceivers support four channels of data in one module, making them suitable for high-density applications, with QSFP+ and QSFP28 supporting 40 Gbps and 100 Gbps, respectively. The C Form-factor Pluggable (CFP) transceivers are designed for high-speed digital signal transmission, supporting data rates up to 100 Gbps.
Optical transceivers offer several key benefits, including high data rates, long-distance transmission, scalability, and low latency. They support data rates ranging from 1 Gbps to 400 Gbps, enabling fast and efficient data transfer. Their ability to transmit data over long distances, up to several kilometres, without significant signal degradation, makes them ideal for wide-area networks (WANs). The modular and hot-swappable nature of optical transceivers allows for easy upgrades and scalability in network infrastructure, while the low latency of optical fibre communication is critical for applications requiring real-time data transmission, such as financial trading and video conferencing. Optical transceivers are used in a variety of applications, including data centers, telecommunications, and enterprise networks.
In data centers, they are essential for connecting servers, storage systems, and networking equipment, ensuring high-speed data transfer and efficient network performance. In telecommunications, optical transceivers are used in backbone networks to transmit data over long distances, supporting high-speed internet and communication services. Businesses use optical transceivers in enterprise networks to connect different parts of their network infrastructure, ensuring reliable and fast communication between departments and locations. The demand for optical transceivers is expected to grow, driven by the increasing need for high-speed data transmission and the expansion of 5G networks. Innovations in optical transceiver technology, such as the development of 800 Gbps transceivers, will further enhance network performance and support the growing data demands of modern applications.
In conclusion, optical transceivers are vital components in today’s communication networks, offering high-speed data transfer, long-distance transmission, and scalability. As technology advances, these devices will continue to play a crucial role in enabling efficient and reliable communication across various industries.