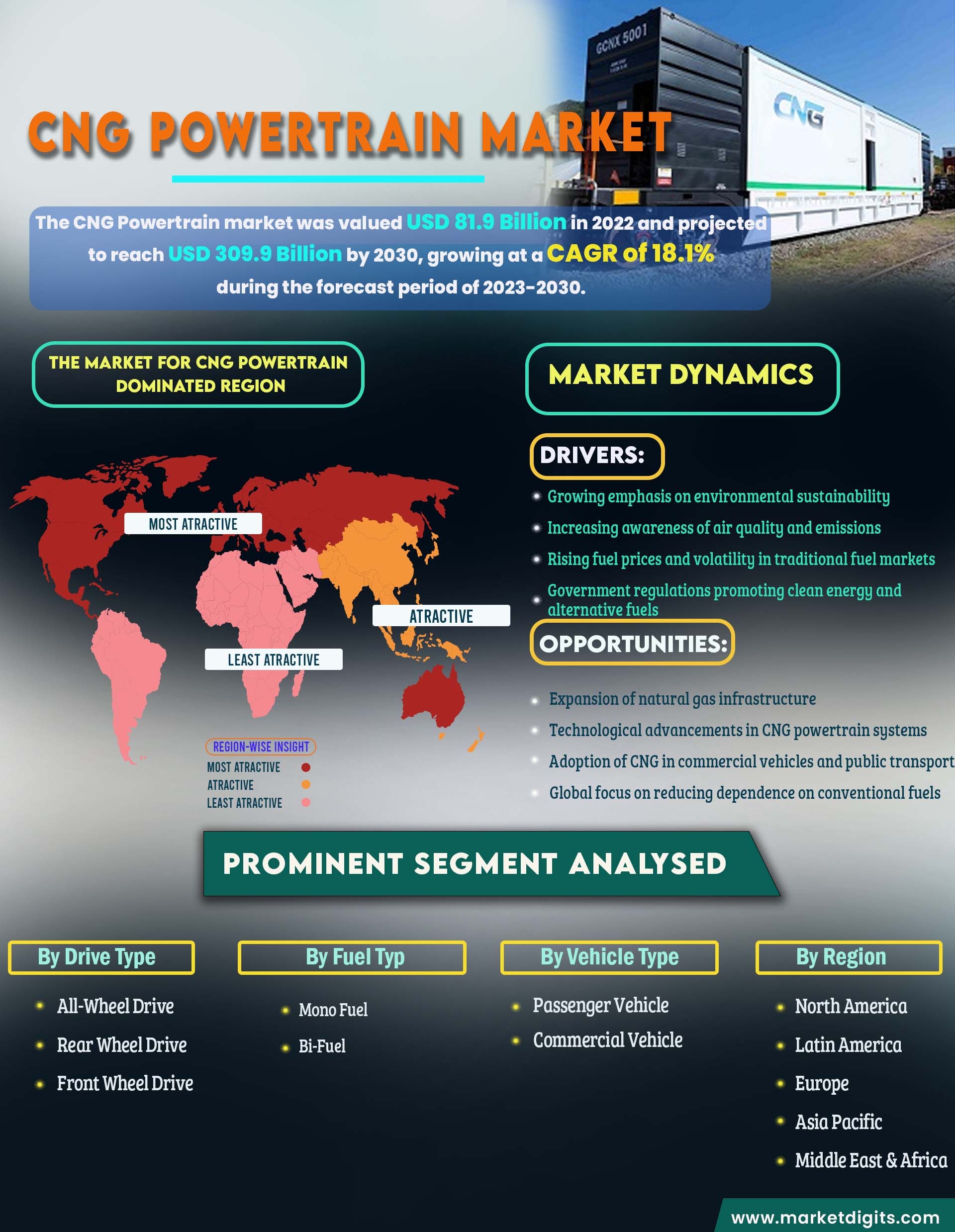
 A CNG (Compressed Natural Gas) powertrain is an eco-friendly alternative to traditional gasoline and diesel engines. It operates by using natural gas stored at high pressure, which is then injected into the engine’s combustion chamber. This type of powertrain is known for its lower emissions, producing significantly fewer pollutants such as CO2 and particulate matter compared to conventional fuels. Vehicles equipped with CNG powertrains are not only environmentally friendly but also cost-effective, as CNG is often cheaper than gasoline or diesel1. Additionally, CNG engines tend to have a longer lifespan due to the cleaner combustion process, which reduces engine wear and tear. The adoption of CNG powertrains is growing, especially in regions with abundant natural gas resources and supportive infrastructure. Automakers are increasingly offering CNG variants of popular models, providing consumers with more choices for sustainable transportation. Despite the benefits, the main challenges include the limited refuelling infrastructure and the reduced driving range compared to gasoline vehicles. However, advancements in technology and increasing investments in CNG infrastructure are expected to mitigate these issues, making CNG powertrains a viable option for the future of green mobility.
A CNG (Compressed Natural Gas) powertrain is an eco-friendly alternative to traditional gasoline and diesel engines. It operates by using natural gas stored at high pressure, which is then injected into the engine’s combustion chamber. This type of powertrain is known for its lower emissions, producing significantly fewer pollutants such as CO2 and particulate matter compared to conventional fuels. Vehicles equipped with CNG powertrains are not only environmentally friendly but also cost-effective, as CNG is often cheaper than gasoline or diesel1. Additionally, CNG engines tend to have a longer lifespan due to the cleaner combustion process, which reduces engine wear and tear. The adoption of CNG powertrains is growing, especially in regions with abundant natural gas resources and supportive infrastructure. Automakers are increasingly offering CNG variants of popular models, providing consumers with more choices for sustainable transportation. Despite the benefits, the main challenges include the limited refuelling infrastructure and the reduced driving range compared to gasoline vehicles. However, advancements in technology and increasing investments in CNG infrastructure are expected to mitigate these issues, making CNG powertrains a viable option for the future of green mobility.
البحث
الأقسام
- Politics
- الرئيسية
- Wellness
- Theater
- Sports
- Shopping
- Religion
- Party
- أخرى
- Networking
- Music
- Literature
- Art
- Health
- Gardening
- الألعاب
- Food
- Fitness
- Film
- Drinks
- Dance
- Crafts
- Causes
إقرأ المزيد
Copper Tube and Fittings Market To Witness Promising Growth Opportunities by 2024 - 2031 | Wieland Group, KME Copper, Mueller Streamline, KOBE STEEL
Copper Tube and Fittings Market report has recently added by Analytic Insights Hub which helps to...
Growth of Data Labeling Solution And Services Market: Key Factors Driving Demand
The global data labeling solutions and services market was valued at approximately USD...
Guanghepaper: Crafting Premium Parchment Paper for Baking Enthusiasts
The journey to baking perfection often begins with the most unassuming tools. Among...
สงครามพอตจิ๋ว! relx รุ่น 6 ปะทะ เยว่เค่อ ใครแน่กว่ากัน?
RELX บุหรี่ไฟฟ้า แชมป์เก่าที่ใครก็รู้จัก
พูดถึงวงการบุหรี่ไฟฟ้า ไม่มีใครไม่รู้จัก relx...

