The global bioresorbable polymers market was valued at USD 1.30 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 13.8% from 2023 to 2030. This expansion is primarily fueled by a rise in consumer health awareness, advancements in healthcare facilities, and an increasing number of surgical procedures. According to the National Library of Medicine (NLM), approximately 310 million major surgeries are performed globally each year, with about 20 million of these in Europe and between 40 to 50 million in the United States. Bioresorbable, or bioabsorbable, polymers belong to a category of materials that can be gradually broken down and absorbed by the body over time.
These polymers find extensive applications across various sectors, with the medical field being a significant area of use. In medicine, bioresorbable polymers are employed in medical devices and implants, including sutures, screws, tissue scaffolds, plates, and stents. Their ability to dissolve within the body over time eliminates the need for additional surgeries to remove them. Furthermore, these polymers are utilized to develop drug delivery systems, such as nanoparticles or microspheres, which release medication at a controlled rate and eventually dissolve in the body, again negating the necessity for removal. By using bioresorbable polymers in medical applications, the risks associated with post-surgery procedures are minimized, benefiting patient outcomes without causing harm to the body.
Gather more insights about the market drivers, restrains and growth of the Bioresorbable Polymers Market
Product Insights
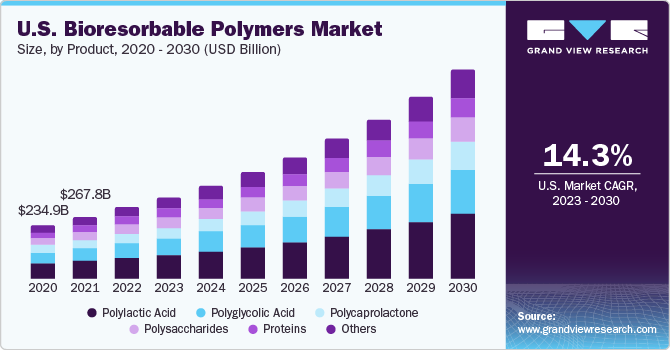
Polylactic acid (PLA) has established itself as the dominant segment within the biopolymer market, securing an impressive 29.5% share of overall revenue in 2022. This material stands out for its unique property of being naturally metabolized into lactic acid within the body at low concentrations. Consequently, it can be safely processed and excreted by the body’s natural elimination systems. This characteristic is particularly beneficial in medical applications, as PLA's biodegradable nature allows it to decompose without the risk of leaving harmful residues. This property eliminates the necessity for secondary surgical procedures typically associated with the removal of non-biodegradable materials.
The increasing adoption of bioresorbable polymer materials like PLA is particularly notable in the field of lumbar interbody fusion, a common surgical procedure for treating spinal issues. PLA is favored due to its mechanical properties, which include significant stiffness, excellent biocompatibility, and a combination of high strength and modulus. These attributes make PLA an ideal candidate for the fabrication of various fixation devices used in orthopedic surgeries, including arrows, washers, pins, and screws. The ability to use materials that do not require surgical removal enhances patient safety and comfort, contributing to the growing preference for PLA in orthopedic applications.
On the other hand, the segment of polyglycolic acid (PGA) is projected to experience robust growth, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 14.1% during the forecast period. This anticipated expansion is largely driven by PGA's rapid degradation rates compared to other biopolymers. This property has spurred increased demand for PGA in diverse drug delivery applications. Specifically, polyglycolic acid is being utilized for the delivery of a variety of therapeutic agents, including proteins, chemotherapeutics, vaccines, analgesics, antibiotics, small interfering RNA (siRNA), and anti-inflammatory medications.
PGA’s versatility is further enhanced by its classification into various forms, such as microcapsules, microspheres, nanofibers, and nanospheres. These classifications are instrumental in optimizing the controlled delivery of adsorbed or encapsulated payloads, thereby improving the efficacy of treatments. The ability to tailor the release profiles of therapeutic agents using PGA makes it a valuable tool in both pharmaceutical and medical applications, ensuring that drugs can be delivered precisely where and when they are needed.
The combination of PLA and PGA represents a significant advancement in the field of bioresorbable materials, addressing both mechanical and biological needs in medical applications. As research and development continue to evolve, it is expected that these materials will play an increasingly critical role in innovative healthcare solutions, providing safe, effective, and patient-friendly alternatives to traditional surgical methods. The growing emphasis on sustainability in materials science also aligns with the natural degradability of these polymers, reinforcing their potential for broader applications in various industries.
Order a free sample PDF of the Bioresorbable Polymers Market Intelligence Study, published by Grand View Research.