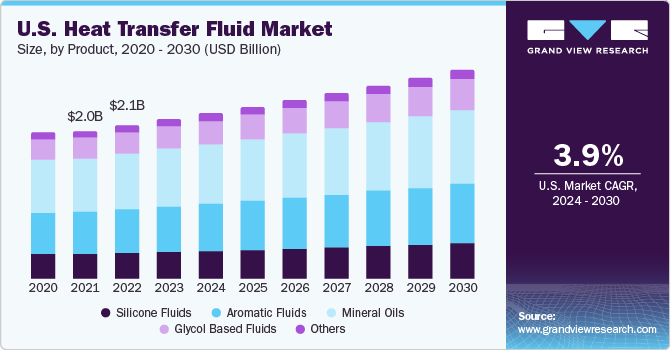
The global heat transfer fluids market was estimated to be valued at approximately USD 11.06 billion in 2023, with expectations to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 3.7% from 2024 to 2030. One of the key factors driving this demand is the rapid adoption of concentrated solar power (CSP) technologies worldwide. Heat transfer fluids (HTFs) are industrial products derived from petroleum sources that play a crucial role in preventing overheating and storing thermal energy. The primary raw materials used in the production of these fluids include crude oil, silica, and base oils. Essential characteristics that define a heat transfer fluid include low viscosity, a non-corrosive nature, high thermal conductivity, high diffusivity, and the ability to withstand extreme phase transition temperatures.
Traditionally, heat transfer fluids have been utilized solely for the purpose of transferring heat to process streams. However, selecting the appropriate HTF is a complex process that involves multiple considerations, such as pumpability, thermal stability, and pressure requirements. The importance of heat transfer fluids is growing, especially in applications like extracting heat from the sun in concentrated solar panels and facilitating gas and oil processing in colder climates.
The COVID-19 pandemic caused significant disruptions in businesses and supply chains globally. The negative repercussions on the oil and gas industry also hindered the growth of the heat transfer fluid market. A decline in both supply and demand for oil and gas—particularly in North America and Europe—halted both onshore and offshore production processes, which adversely affected the heat transfer fluids market. Moreover, the suspension of new solar power project installations and disruptions in the operations of existing plants further obstructed market growth.
Gather more insights about the market drivers, restrains and growth of the Heat Transfer Fluids Market
Market Concentration and Characteristics
The heat transfer fluids market is moderately consolidated, featuring the presence of several large players, including Dow Inc., Exxon Mobil Corporation, British Petroleum, Eastman Chemical Company, and Royal Dutch Shell. To navigate competitive pressures, market players are adopting product differentiation strategies that help them avoid price wars.
There has been a high level of merger and acquisition activity in the market over the past few years. For example, Indian oil and gas producer Oil & Natural Gas Corp (ONGC) successfully acquired Hindustan Petroleum Co. Ltd. (HPCL) by purchasing 51.11% of its shares, becoming the first vertically integrated oil manufacturer in the country. Such strategic moves by key companies around the world illustrate their operational strategies aimed at maintaining sustainability and competitiveness within the global heat transfer fluids ecosystem.
Companies operating in the heat transfer fluids market are highly competitive and well-integrated along the value chain. A comprehensive analysis of 24 leading producers worldwide has shown that nearly 55% of heat transfer fluid manufacturers are also engaged in the captive production of basic raw materials and allied feedstock.
An important aspect of competition within the industry is the variety of product offerings. On average, companies provide around seven different variants of heat transfer fluids, with Dynalene, Dow, Radco Industries, BASF, and Eastman being notable for offering the highest number of products in the marketplace. In contrast, smaller-scale companies often focus on specialized offerings, with their heat transfer fluid products catering to a broader temperature range and a diverse customer base at the national level.
Order a free sample PDF of the Heat Transfer Fluids Market Intelligence Study, published by Grand View Research.