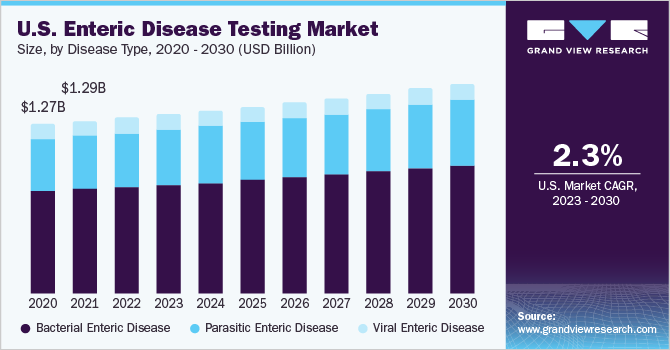
The global enteric disease testing market was valued at approximately USD 3.81 billion in 2022 and is projected to experience growth at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 2.7% from 2023 to 2030. Key drivers behind this market expansion include ongoing technological advancements and supportive government funding, particularly in emerging economies. Furthermore, there is an increasing global demand for early diagnostic solutions, which is expected to enhance the relevance and applicability of this market, further fueling its growth.
During the COVID-19 pandemic, there was heightened awareness surrounding viral and bacterial infections, prompting individuals to prioritize the consumption of home-cooked and hygienic food to mitigate the risk of infections. As a result, there was a noticeable decline in the incidence of enteric diseases, which led to a subsequent decrease in the demand for enteric disease testing during 2020 and 2021. Additionally, testing for COVID-19 took precedence during the pandemic, overshadowing testing for other infectious diseases. This shift negatively impacted the demand for enteric disease testing products, which in turn hindered overall market growth.
In various regions, particularly Asia, Africa, and Latin America, the prevalence of enteric infections such as salmonella, campylobacter, Escherichia coli, and norovirus remains alarmingly high. According to the National Library of Medicine, as of 2018, enteric fever in these regions was associated with a case fatality rate of approximately 1%. Consequently, there is a growing demand for enteric disease testing to facilitate accurate and timely diagnoses.
Gather more insights about the market drivers, restrains and growth of the Enteric Disease Testing Market
Initial symptoms linked to enteric diseases often include abdominal cramps, vomiting, nausea, and anorexia. If left untreated, these symptoms can escalate into severe conditions characterized by significant fluid and nutrient loss from the body. Vulnerable populations, particularly children and the elderly, are particularly susceptible to these diseases due to their compromised immune systems. According to the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation, approximately 500,000 young children under the age of 5 succumb to enteric and diarrheal diseases each year, primarily in developing countries. Furthermore, an estimated 25,000 children lose their lives to enteric fever annually, with the majority of cases occurring in regions lacking access to safe water and adequate sanitation facilities.
The mild initial symptoms of enteric diseases can often be overlooked, posing a significant barrier to effective market growth. These diseases have emerged as a leading cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide, especially in developing nations where drainage and sanitation infrastructure is insufficient. It is estimated that developing countries contribute to over 85% of total enteric infection cases in terms of incidence and epidemiology.
As the incidence of enteric diseases continues to rise, coupled with the cost-effectiveness of advanced diagnostic systems, the demand for early diagnosis is expected to increase. For example, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, salmonella bacteria are responsible for approximately 1.35 million infections, around 26,500 hospitalizations, and roughly 420 deaths each year in the United States. The increasing prevalence of enteric diseases in developing economies, combined with inadequate laboratory settings and limited public awareness, represents a largely untapped market. According to Foundation Merieux, enteric diseases rank as the second leading cause of death among children under 5 years old in Asian and African countries.
Order a free sample PDF of the Enteric Disease Testing Market Intelligence Study, published by Grand View Research.