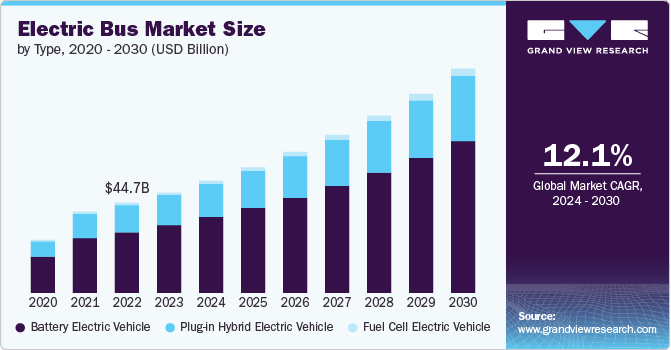
The global electric bus market was valued at USD 49.81 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 12.1% from 2024 to 2030. This growth is being driven by the increasing adoption of electric buses, largely due to rising environmental concerns and strong government support. Electric buses offer a number of advantages over traditional gasoline and diesel-powered buses, including zero tailpipe emissions, which help reduce air pollution. Moreover, they are considered cleaner and more environmentally friendly than conventional buses, aligning with global efforts to tackle climate change and reduce carbon footprints.
In addition to their environmental benefits, electric buses provide a quieter and smoother ride compared to diesel buses. This reduction in noise pollution not only benefits urban environments but also enhances driver awareness and passenger comfort. Quieter vehicles help reduce the stress and noise levels in crowded urban areas, contributing to a more pleasant and healthier transportation experience. As cities and governments place greater emphasis on sustainable urban mobility and cleaner air, the demand for electric buses is expected to continue growing throughout the forecast period from 2024 to 2030.
Gather more insights about the market drivers, restrains and growth of the Electric Bus Market
Type Insights
The electric bus market is broadly categorized into two main types: Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs) and Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles (FCEVs). Among these, the Battery Electric Vehicle (BEV) segment dominated the market in 2023, accounting for a significant 67.6% of the total revenue. BEVs are considered a more efficient and cost-effective alternative to traditional fuel-powered buses. These buses run entirely on electricity stored in batteries, making them a zero-emission solution for public transportation.
The primary advantages of BEVs over conventional diesel or gasoline-powered buses include lower operational costs, reduced maintenance requirements, and easier charging infrastructure. BEVs are generally more energy-efficient, providing cost savings over time for transit authorities. Additionally, they are easier and less expensive to charge compared to fuel-powered buses, which require more complex fueling infrastructure. The relatively low cost of electricity and the efficiency of modern battery technology have made BEVs a preferred choice for many municipalities looking to modernize their fleets with environmentally friendly alternatives. As more cities and countries focus on reducing their carbon emissions, the adoption of BEVs is expected to remain strong, driving the growth of the segment.
The Fuel Cell Electric Vehicle (FCEV) segment, while smaller in comparison to BEVs, is projected to experience significant growth during the forecast period from 2024 to 2030. FCEVs are powered by hydrogen fuel cells, which produce electricity by combining hydrogen with oxygen in a chemical reaction. This technology offers a significant reduction in greenhouse gas emissions and air pollutants compared to traditional fossil fuel-powered vehicles. Since the only byproduct of hydrogen fuel cells is water vapor, FCEVs are considered an environmentally friendly and sustainable transportation solution.
The growing interest in FCEVs can be attributed to several factors. First, the infrastructure for hydrogen fueling is expanding, with more refueling stations being built globally, making it more feasible for cities and transit authorities to adopt FCEVs. Second, hydrogen fuel cells offer longer driving ranges and faster refueling times compared to battery electric buses, which could make them more suitable for certain use cases, such as long-distance routes or operations in areas with limited charging infrastructure. Additionally, FCEVs contribute to reducing dependence on fossil fuels, which is in line with global efforts to transition toward cleaner energy sources.
Government initiatives also play a crucial role in the growth of the FCEV market. Policies and programs that encourage the adoption of hydrogen fuel cell technology are helping to accelerate the development and deployment of these vehicles. For instance, the Electric Vehicles (EVs) Initiative, coordinated by the International Energy Agency (IEA), is a multi-government policy forum aimed at promoting electric vehicle adoption worldwide. This initiative supports member governments in their efforts to create favorable conditions for the widespread adoption of both BEVs and FCEVs, which is expected to positively impact the market for hydrogen-powered electric buses.
Order a free sample PDF of the Electric Bus Market Intelligence Study, published by Grand View Research.